Important things to know about ETL | Uses Of ETL Tool
ETL stands
for Extract, Transform, and Load. It is a process of extracting data from
various sources, transforming it into a format that can be easily used for
analysis, and loading it into a target database or data warehouse.
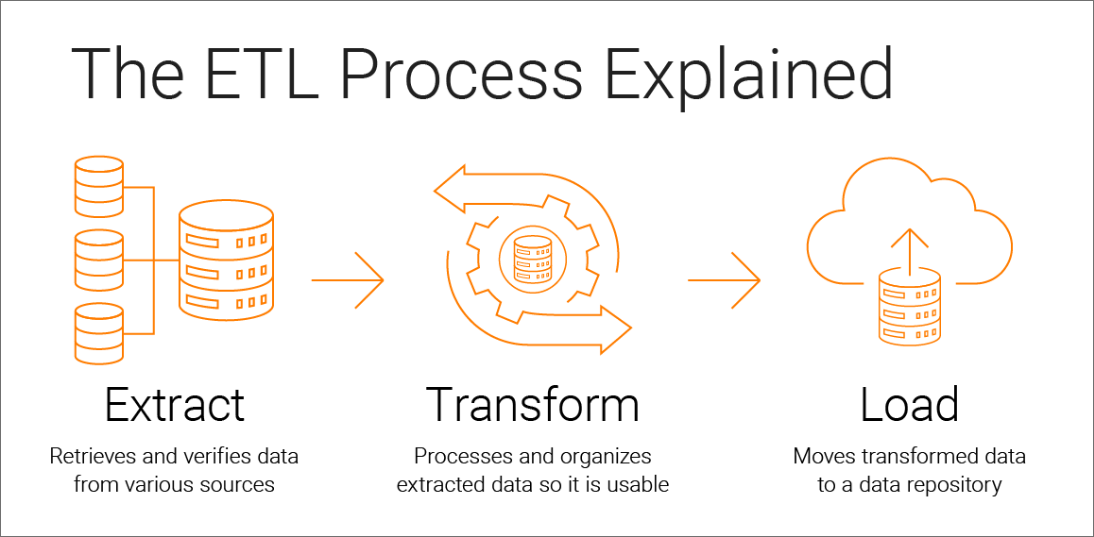
The ETL
process involves several steps, including:
Extraction:
The data is extracted from various sources, such as databases, flat files, or
web services.
Transformation:
The extracted data is transformed into a format that can be easily used for
analysis. This includes data cleaning, data integration, and data enrichment.
Loading:
The transformed data is loaded into a target database or data warehouse. This
step involves mapping the data to the appropriate fields in the target system
and validating the data before loading.
The ETL
process is critical in data integration and business intelligence. It allows
organizations to consolidate data from various sources, transform it into a
format that can be easily analyzed, and load it into a central repository for
reporting and analysis.
Uses of ETL
ETL has
several important uses, including:
Data
integration: ETL is used to integrate data from multiple sources into a single,
centralized repository. This allows organizations to combine data from
different systems, such as customer data, sales data, and inventory data, and
create a unified view of their business.
Business
intelligence: ETL is used to transform raw data into a format that can be
easily analyzed by business intelligence tools. This includes data cleaning,
data integration, and data enrichment to ensure that the data is accurate, complete,
and consistent.
Data
warehousing: ETL is a key component of data warehousing, which involves storing
large amounts of historical data in a central repository for analysis. ETL is
used to extract data from various sources, transform it into a format that can
be easily analyzed, and load it into a data warehouse.
Data
migration: ETL is used to migrate data from one system to another. This is
commonly used when organizations switch to a new software system or upgrade
their existing systems.
Overall,
ETL is a critical process in modern data management and analysis. It enables
organizations to consolidate data from various sources, transform it into a
format that can be easily analyzed, and load it into a central repository for
reporting and analysis.
Pros & Cons of ETL
Tool
Pros of ETL tools:
Automation:
ETL tools automate the extraction, transformation, and loading of data, which
reduces the time and effort required for manual data integration.
Scalability:
ETL tools can handle large volumes of data from multiple sources, making them
ideal for organizations with complex data environments.
Data
quality: ETL tools can perform data cleansing and transformation, ensuring that
the data is accurate, consistent, and complete.
Reusability:
ETL tools enable the reuse of data integration processes, reducing the time and
effort required for future data integration projects.
Cons of ETL tools:
Complexity:
ETL tools can be complex to configure and maintain, requiring specialized
knowledge and expertise.
Cost: ETL
tools can be expensive, especially for organizations with large data volumes.
Integration
challenges: ETL tools may not be able to integrate with all data sources, which
can lead to challenges when integrating data from diverse sources.
Performance
issues: ETL tools can sometimes result in performance issues, such as slow data
processing or data latency.
In summary,
while ETL tools offer many benefits such as automation, scalability, data
quality, and reusability, they can also be complex, expensive, and have
integration and performance challenges. The decision to use ETL tools should be
based on a thorough evaluation of the organization's data management needs and
available resources.